Mobile applications have changed the way people connect, shop, communicate, and engage with digital content. Every time a user opens an app, sends a message, fetches data, or switches devices, a hidden system works quietly in the background to ensure everything runs smoothly. That system is the app’s backend. Acting as the invisible engine behind every interaction, the backend keeps the experience fast, reliable, secure, and consistent. Even the most visually appealing app cannot deliver lasting value without a strong backend supporting its operations. Crafting a reliable backend is more than just a technical task; it’s a strategic foundation that influences how well the app performs, how easily it scales, and how effectively it handles user data. As apps grow more complex and attract larger user bases, the importance of having a dependable backend only increases. Businesses aiming to offer seamless, responsive, and secure app experiences must understand what goes into building the right infrastructure. In this blog, we’ll delve into what backend development really means, explore the core components of mobile backend architecture, walk through the process of building a backend for an app, and highlight key mistakes developers should avoid.
What is Backend Development?
Backend development refers to everything that happens on the server side of a mobile application. While users interact with the interface on their devices, the backend handles processing, storage, security, and data flow behind the scenes. Backend developers write the logic that connects the mobile front end to the server and database. They are responsible for structuring how the data is received, processed, stored, and returned to the user interface.
The backend system is typically composed of servers, databases, middleware, APIs, and cloud infrastructure. These components work together to ensure that every user interaction is processed quickly and securely. For example, when a user logs into an app, the backend authenticates their credentials, pulls data from the database, and sends it back to the user interface in milliseconds.
Core Components of Mobile Application Backend Architecture
The strength and flexibility of any mobile app heavily depend on its backend architecture. A successful backend is built with a carefully chosen mix of components, each playing a distinct role in how the app functions, performs, and scales. Understanding these components helps developers and stakeholders make smarter decisions when designing or improving backend systems.
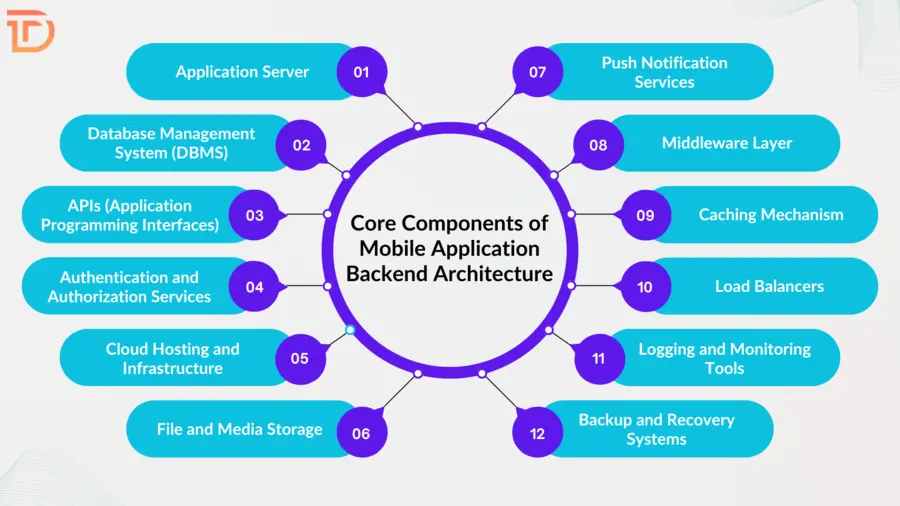
- Application Server: The application server is the command center that processes request and executes the app’s logic. When users perform actions on the front end, the server interprets those commands and performs the necessary operations. Whether it’s managing sessions, processing payments, or fetching user profiles, the server ensures these tasks happen efficiently and accurately.
- Database Management System (DBMS): All persistent data in a mobile app lives in the database. It holds everything from user credentials and messages to app settings and transaction histories. A well-structured DBMS supports smooth data querying, indexing, and updating. Developers must decide between relational systems like SQL, which use structured tables, or NoSQL databases, which allow flexible data storage formats ideal for evolving applications.
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): APIs form the bridges between the mobile app and backend services. They allow the app to communicate with internal databases or third-party platforms like maps, analytics, or social media. APIs must be secure, efficient, and well-documented to maintain smooth interactions between all systems connected to the app.
- Authentication and Authorization Services: Security begins with identifying users and controlling their access. These services confirm user identities through methods like passwords, biometrics, or tokens. Once verified, authorization rules determine what actions each user can perform. A solid system protects sensitive data and prevents misuse or unauthorized access.
- Cloud Hosting and Infrastructure: Cloud services provide the environment where backend components live. These platforms offer flexibility to scale resources based on demand. Instead of relying on fixed physical servers, cloud infrastructure allows apps to run more reliably across different regions, ensuring performance remains strong even under heavy user traffic.
- File and Media Storage: Apps that handle photos, videos, documents, or audio files need a dedicated space to store and retrieve these assets. A reliable storage system allows fast access while keeping files safe and organized. Cloud storage solutions also provide automatic backups, versioning, and secure delivery.
- Push Notification Services: Keeping users engaged often depends on timely alerts. Push notification services allow apps to send personalized messages to users even when the app is closed. These messages may remind users of updates, prompt them to complete actions, or deliver promotions, helping improve user retention and engagement.
- Middleware Layer: Middleware acts as a translator between the application and other backend services. It applies business logic, manages data formatting, handles caching, and controls communication between systems. Middleware makes the app more modular and easier to maintain, especially as more services get added over time.
- Caching Mechanism: Caching stores frequently accessed data temporarily to reduce database queries and improve response time. It enhances user experience by loading content faster and reducing the load on backend servers. Proper cache management ensures data remains fresh while still delivering speed.
- Load Balancers: As apps grow, they face increased traffic. Load balancers distribute incoming requests across multiple servers to avoid overloading one system. They improve performance, enhance reliability, and provide failover protection if one server goes down. Load balancing becomes essential for high-traffic applications.
- Logging and Monitoring Tools: Every backend needs a way to track its health and performance. Logging captures events like errors or system changes, while monitoring tools watch metrics such as CPU usage, response time, and server uptime. These tools help detect issues early and allow quick fixes before users are impacted.
- Backup and Recovery Systems: Unexpected failures can lead to data loss without proper backups. A solid backup strategy ensures copies of databases, configurations, and media are always available. Recovery systems make it possible to restore service quickly after disruptions, protecting both users and business operations.
Each of these backend components adds a layer of functionality, stability, or protection to a mobile app. Together, they form the architecture that ensures the app can deliver seamless, fast, and secure experiences to users no matter how complex the requirements become.
How to Build a Backend for a Mobile App?
The right backend can make a mobile app fast, stable, and user-friendly. Building one requires a systematic approach with attention to detail. Below are the steps involved in backend creation:
- Define Functional Requirements: Start by understanding what the backend needs to support. Identify all server-side tasks such as user management, data syncing, file storage, notifications, and integration with other systems. Clearly listing these functions helps developers design the right architecture from the beginning. Well-defined requirements reduce guesswork and make development more focused and efficient.
- Choose the Right Tech Stack: Select programming languages, frameworks, databases, and hosting solutions that meet the app’s performance needs and long-term vision. Some stacks are better for rapid development, while others offer stronger security or scalability. Consider how many users the app will support, the type of data involved, and what tools your team already knows.
- Set Up a Scalable Server: Build a server environment that can handle increasing user activity without slowing down. Cloud platforms are useful for this, offering automatic scaling and flexible resource allocation. A good setup should also include load balancers, caching, and backup systems to keep the backend stable during traffic spikes and system updates.
- Design the Database Structure: Think carefully about how data will be organized, retrieved, and stored. Relational databases are ideal when data needs to be structured and consistent, while NoSQL databases suit apps needing flexibility. Clean schema design, indexing, and normalization reduce redundancy, speed up queries, and improve overall app performance over time.
- Develop and Test APIs: Create APIs that allow the app to communicate with the backend safely and reliably. Each API should perform a specific task like login, data fetch, or file upload. Thorough testing across devices and conditions ensures that everything works well. Clear documentation and version control make future updates easier to manage.
- Implement Security Protocols: Protect user data through encryption, secure tokens, and safe transmission methods. Use HTTPS for all communication between the app and server. Add features like two-factor authentication, role-based access, and regular security audits. Maintaining secure backups and logging access activity also helps reduce the risks of data loss or breaches.
- Monitor and Optimize Performance: Keep track of how the backend behaves once it goes live. Use real-time monitoring tools to catch issues such as slow responses, server overload, or API failures. Address problems as they appear and update the system regularly. Performance tuning makes the app feel smooth and keeps users satisfied over time.
Avoiding Common Development Pitfalls
While backend development offers endless possibilities, it also comes with risks that can lead to poor user experience or system failure. Avoid these frequent mistakes to ensure a stable and secure backend:
- Ignoring Scalability from the Start: Focusing only on immediate needs often backfires as user numbers increase. Systems designed without scaling in mind may crash under pressure. Always plan for higher traffic with flexible server setups, scalable databases, and resource allocation that adjusts as your app grows.
- Weak Security Implementation: Leaving out security practices makes your backend vulnerable to attacks. Data should be encrypted during storage and transmission. Input validation, secure APIs, and proper user authentication help protect the system from common threats like injections or unauthorized access.
- Poor API Design and Documentation: Confusing or inconsistent APIs frustrate developers and increase bugs. Every endpoint should be clearly defined with expected inputs, outputs, and error responses. Providing complete documentation ensures faster integration, easier debugging, and smoother updates across different development teams.
- Overcomplicated Database Models: Designing overly complex schemas can slow down queries and make the database hard to maintain. Too many joins or deeply nested objects lead to performance bottlenecks. Keep structures clean, index wisely, and focus on fast, scalable data operations.
- Lack of Load Testing: Skipping load tests leaves systems unprepared for traffic spikes. Realistic testing helps identify weak points before they become problems. Simulate different user volumes and actions to see how the backend responds, then optimize performance before launch.
- Not Using Version Control Properly: Without proper version control, teams can accidentally overwrite code, introduce bugs, or break stable features. Structured commits, clear branches, and tagging versions help manage changes, track progress, and roll back when necessary, without losing critical work.
- Forgetting Error Handling and Logging: Missing or vague error messages make issues harder to fix. Use structured logging to track backend activity and design helpful error responses. This makes it easier to spot bugs, resolve failures, and keep the user experience stable during disruptions.
Way Forward
Success in mobile app development depends on building a backend that is fast, secure, scalable, and flexible enough to grow with user demands and changing technologies. A strong backend manages traffic spikes, protects data, supports new features, and keeps the app running smoothly across all devices. The most engaging apps all share a common foundation: reliable backend infrastructure that handles pressure without compromising performance. Choosing the right architecture, tools, and practices sets the stage for everything that follows. Teams that focus on backend strength can innovate confidently, fix issues quickly, and deliver features that users love. Every interaction depends on that invisible layer working perfectly behind the scenes. A well-planned backend is not just a requirement; it is the foundation of a stable, user-friendly mobile app.
For businesses aiming to build reliable and future-ready mobile apps, Dreamer Technoland offers reliable backend development services tailored to your needs. With more than 10 years of experience, our team focuses on creating stable, high-performance infrastructures that ensure fast response times, smooth data handling, and easy scalability. From architecture planning to deployment and optimization, we handle every step with precision, so your app remains secure, responsive, and prepared for growth. Let us help you power your mobile app with a backend that performs flawlessly today and adapts effortlessly tomorrow.