Rapid changes in technology force development teams to stay agile and forward-thinking. With each passing year, emerging tools, frameworks, and methodologies reshape how software is developed, deployed, and maintained. The pace of technological evolution is relentless, with new innovations constantly challenging the traditional development paradigms. Developers and organizations that are proactive in understanding and adopting these current trends can unlock a wealth of opportunities to create top tier solutions, streamline workflows, and ultimately stay ahead of the competition. By embracing the right tools and strategies, they can not only optimize the efficiency of their development processes but also future-proof their efforts, ensuring that their products are adaptable and scalable in an ever-changing landscape. In this blog, we will discuss what software development trends mean, explore the top ten latest trends in software development, and examine the key challenges in adapting to rapid innovation.
Trends in Software Development: What Does It Mean?
Software development trends represent shifts in tools, techniques, and priorities across the design, creation, deployment, and maintenance of applications. Each trend reflects new demands from users, market requirements, and technological advances. Recognizing these patterns enables teams to make informed decisions about architecture, tools, and skills. Adaptation becomes essential to staying competitive, improving efficiency, and fostering innovation.
Top 10 Current Software Industry Trends
Software development continues to evolve at a fast pace, shaped by innovation, user behavior, and the rising demand for intelligent digital solutions. Developers and organizations must remain flexible, adopt relevant tools, and understand which trends carry long-term value. The following are the most impactful trends currently transforming the software development landscape.

Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML)
AI and ML are powering smarter applications capable of learning from data, identifying patterns, and making accurate predictions. These technologies are embedded in voice assistants, fraud detection systems, recommendation engines, and business analytics platforms. Developers now rely on pre-built models or train custom ones to personalize experiences and automate decisions. As AI capabilities grow, its integration into everyday software will only become more widespread, practical, and necessary for competitive success.
AR/VR and Immersive Experiences
Interactive digital environments are now used in training, virtual shopping, product demos, and real-time collaboration. Augmented reality overlays content onto the real world, while virtual reality immerses users in entirely digital spaces. Developers use toolkits like ARKit and Unity to design these experiences across web and mobile platforms. AR/VR improves user engagement and allows businesses to offer hands-on experiences without physical presence. Accessibility, reduced hardware costs, and content richness drive adoption.
Blockchain and Decentralized Applications
Blockchain’s secure and transparent nature is being adopted beyond cryptocurrencies. Smart contracts automate processes, while decentralized apps (dApps) enable peer-to-peer interactions without central control. Use cases include supply chain verification, digital identity, and ownership tracking. Developers work with platforms like Ethereum and Hyperledger to build tamper-proof systems. Blockchain introduces new possibilities in trust, traceability, and decentralization, especially in industries where security, auditability, and data integrity are non-negotiable priorities.
Microservices and Containerization
Breaking down monolithic applications into microservices improves flexibility, performance, and scalability. Each service handles a specific function and communicates with others through lightweight APIs. Docker simplifies packaging, while Kubernetes orchestrates deployment and scaling. This architecture supports faster releases and easier debugging. Developers gain more control over updates, while businesses benefit from reduced downtime and enhanced agility. Microservices also allow the use of different technologies within the same project without conflict.
Edge Computing
Shifting data processing closer to the source boosts performance and lowers dependence on centralized cloud servers. Edge computing supports real-time responses, especially in connected devices, autonomous systems, and sensor-based applications. Industries like healthcare, retail, and logistics use it to ensure fast decisions without delay. Developers design for local processing capabilities while managing synchronization with the cloud. As user expectations grow, edge computing becomes crucial for responsive, always-available digital services.
Low-Code and No-Code Development
Drag-and-drop interfaces and pre-configured modules help users build software without needing to write full code. These platforms enable faster MVP creation, quicker iterations, and simpler automation of internal workflows. Developers also use low-code tools to speed up basic tasks, focusing their efforts on complex problems. Organizations benefit from reduced development costs and better collaboration between technical and non-technical teams. Low-code is turning software development into a more accessible process.
Observability and Cloud Native Monitoring
With distributed systems running across multiple environments, observability ensures teams can detect and resolve issues before users are affected. Logs, metrics, and traces are analyzed in real-time to identify performance slowdowns or failures. Tools like Grafana and Prometheus give developers deep insights into system health. Observability helps teams understand behavior across microservices, databases, and APIs, leading to quicker fixes and more reliable software that performs well in every scenario.
DevSecOps and Continuous Security
Embedding security checks into the software development lifecycle helps teams catch vulnerabilities early. Automated tools monitor code quality, scan dependencies, and enforce policy compliance during every deployment stage. DevSecOps promotes collaboration between developers, operations, and security experts. Continuous threat detection reduces risk exposure while ensuring speed and compliance. With rising cyber threats, integrating security throughout the pipeline is now essential to maintaining user trust and protecting sensitive data at all times.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
PWAs provide fast, engaging web experiences that feel like native apps. They load instantly, work offline, and support push notifications. Businesses use them to reach more users without building separate Android and iOS apps. Developers benefit from faster deployment and single-codebase management. PWAs improve mobile accessibility while reducing the cost of maintenance. As more users access services through mobile browsers, PWAs are becoming a practical solution for scalable user engagement.
Quantum Computing Readiness
Quantum computing is still emerging, but software development is preparing for its future impact. Developers explore new languages like Q#, Cirq, and Qiskit to simulate quantum logic. Potential applications include complex simulations, data encryption, and logistics optimization. Though full-scale adoption remains years away, experimenting today provides a head start. Understanding quantum computing’s potential allows teams to assess risks and opportunities and align long-term strategies with this future technology.
Challenges in Adapting to Rapid Technological Shifts
Technological advancements bring new capabilities, but they also introduce significant complexity into the software development process. Teams must continuously adjust to stay competitive without disrupting existing workflows. Balancing innovation with reliability becomes the cornerstone of sustainable progress in fast-moving environments. Here are the core challenges organizations encounter while adapting to rapid shifts in software technologies.
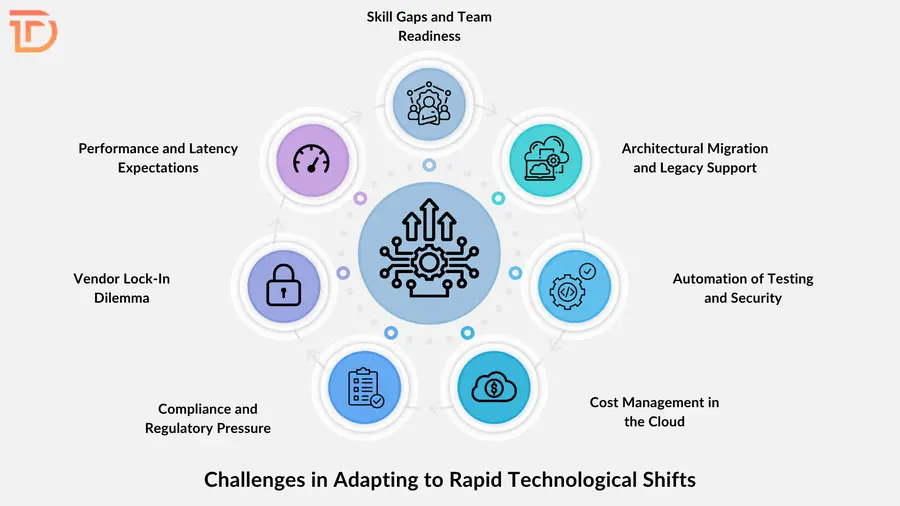
Skill Gaps and Team Readiness
Adopting modern technologies requires far more than just tools. It demands reskilling teams, updating internal knowledge, and realigning workflows across engineering, QA, and DevOps. The transition often reveals gaps that delay project execution, especially when foundational understanding or hands-on experience is limited within the existing workforce.
Architectural Migration and Legacy Support
Transforming legacy applications into microservices or cloud-native frameworks poses both technical and operational risks. Large-scale refactoring needs meticulous planning to avoid disruption. At the same time, maintaining backward compatibility with legacy systems involves added development overhead and often slows down the speed of innovation across enterprise environments.
Automation of Testing and Security
Modern delivery pipelines require automated validation at every stage to prevent regression and security loopholes. Scaling unit, integration, and penetration testing to match rapid deployment cycles can be difficult without reliable test suites. Delays in automation often result in bugs, vulnerabilities, and costly fixes post-release, increasing technical debt.
Cost Management in the Cloud
Cloud platforms offer flexibility, but poor monitoring or lack of resource control can lead to unanticipated billing spikes. Managing compute instances, storage, and third-party services demands strict governance policies. Without real-time insights and budgeting mechanisms, organizations struggle to maintain predictable costs across evolving multi-cloud environments.
Compliance and Regulatory Pressure
Adhering to global data privacy laws and industry-specific standards presents ongoing challenges. Frequent policy changes demand continuous auditing, documentation, and tool upgrades. Teams must build automated workflows to ensure compliance without slowing down releases. Misalignment with regulations can lead to legal consequences or reputational damage in sensitive sectors.
Vendor Lock-In Dilemma
Relying heavily on a single cloud provider or proprietary development tool increases the risk of inflexibility. Moving to another platform often involves data migration, code rewrites, and architectural adjustments. Many organizations now favor open-source tools or hybrid strategies to maintain freedom of choice and long-term adaptability.
Performance and Latency Expectations
Modern users expect lightning-fast interactions, regardless of location or device. Delivering this performance consistently requires optimized delivery pipelines, global edge networks, and finely tuned backend processes. Balancing responsiveness with system complexity forces engineers to make careful architectural decisions that influence scalability and long-term maintenance.
Summing Up Everything
Understanding current trends in software development equips teams to build systems that last and adapt. Artificial intelligence, microservices, edge computing, and immersive technologies represent more than buzzwords. They offer real-world advantages in speed, efficiency, and user experience. Challenges such as skill shortages, legacy integration, cost control, and regulatory concerns must be addressed proactively through strategic governance and architectural planning.
Dreamer Technoland specializes in guiding businesses through these technical transformations. With custom software development services spanning AI integration, microservices design, secure cloud deployments, and emerging technology adoption, we empower startups and established businesses to leverage modern trends effectively. Our focus on collaboration and innovation ensures solutions fit each company’s goals and position them for long-term success in an evolving digital landscape.